According to the statistics by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 1/3rd of the total food produced for human consumption goes to waste. This accounts for more than 1.5 billion tonnes of food going to waste in the world today which is a staggering number!
As per the Economic Research Survey (ERS), United States Department of Agriculture USDA reported nearly 12.3% of the US was food insecure at some point in 2016. This raises serious concerns provided the gravity of the situation. With food insecurity looming communities worldwide, preventing world hunger has been identified as a key global development goal.
And a large part of this problem is contributed from the consumer side of the food supply chain.
Today, technology enables anyone with a smartphone and internet to develop applications that can help solve global level issues. A number of driven companies within the food & beverages manufacturing / CPG retail space have committed resources to providing solutions that deal with the issue of ‘food safety and management’
We have already talked about how IoT Platforms can play a role in recycling and smarter waste management.
When it comes to food waste management, the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) is being applied to build platforms which combine quality assurance, traceability, food safety, food sharing & recycling, and vendor management, etc. into one digital centralized platform where data can be gathered and used to make things more efficient.
Manufacturers are investing in building smarter processes, applications and robust IoT Platforms to ensure sustainable and productive models of food management.
“Investing in Technology infrastructures instead of training workforces is the new normal in the age of IoT”
For instance, USDA’s Foodkeeper app that allows users to understand and maximize the freshness and quality of items or UK based Too Good to Go which provides stores and supermarkets with their cloud-based platform in order to manage and sell their surplus at discounted prices.
Or take PareUp for example, which connects consumers to retailers in the New York City. By browsing and purchasing the food which is nearing its expiration date at discounted prices, PareUp App benefits both consumers and retailers.
Or the UK based FreeMeal Swap, which connects consumers to share excess food or ‘leftovers’ with other members of the community.
Let’s look at Ireland’s FoodCloud.

FoodCloud
Food Cloud has developed ‘FoodCloud Hubs’ to work with business, manufacturers, distributors, charities, and supermarts to manage the supply of surplus. With the help of data analysis and an IoT based platform, FoodCloud provides efficient farm to fork solution for the storage and distribution of surplus food around Ireland.
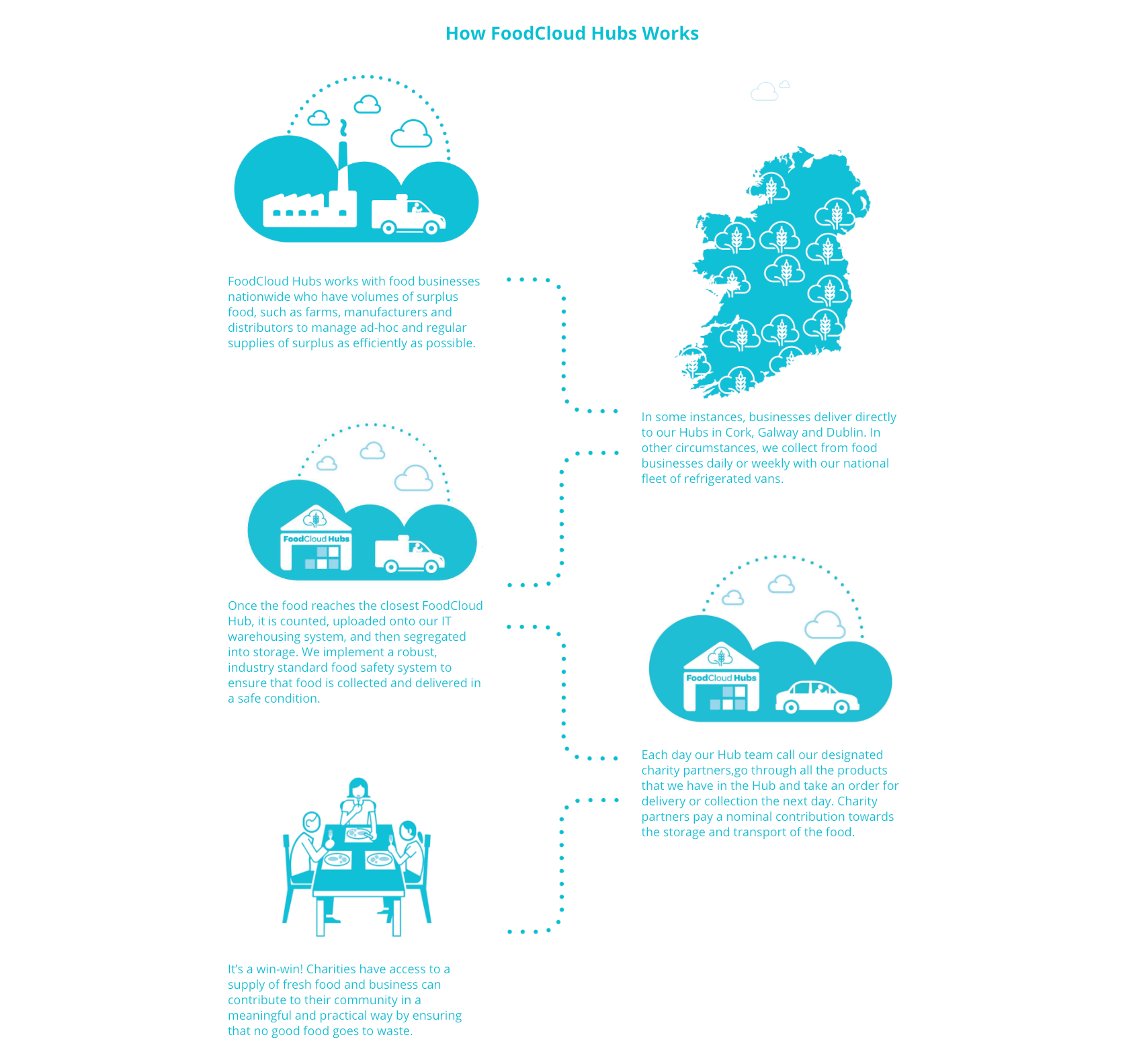
How Food Cloud Hubs Work (Source: FoodCloud’s Website)
IoT and Food Security
If the CPG industry can leverage IoT platforms and technology to digitize their product data on a serial level or batch level and update those instances as they move along the supply chain, it could provide very detailed data on the “location” and “status” of those products in relation to the “Product Expiry Date”.
For example: If we were to run a trace on a particular batch of peanut butter jars and trace discover their status as “In Storage” at the retailers’ location just 3 weeks before the expiry date, we can safely assume that batch is not going to be sold and is heading towards waste disposal in 3 weeks. Those insights could enable the company to flag that batch for transport to a food security program elsewhere where it could be consumed rather than disposed as waste.
Similarly, a consumer at home could scan the peanut butter jar at a serial level, view insights into how much longer that product will remain safe for consumption on their shelf and take a call on whether they can consume it on time or drop it off someplace responsible for food security programmes. This enables consumers to make decisions on an individual level.
IoT enabled applications support high-quality data analysis aimed at refining and optimizing operation processes and changing food waste to food security is an area that can significantly benefit from IoT technologies, traceability and offering insights into the movement of food products.



